
Tag Archives: 2016
Velocity-Time Graph of Parachute Jump

Physics around us
Waves Summary

Click here to view the simulations transverse and longitudinal waves
Students are confused when they need to visualise what is the direction of the particles the next moment of the wave. There is a simpler way solve such question.

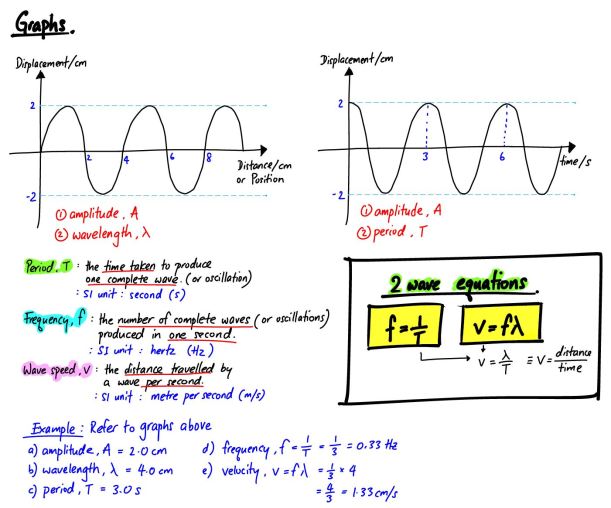
Click here to view another example on graphs

Click here to know more about wavefronts created in a ripple tank.
Thermal Properties of Matter







Thermal Transfer Summary and Applications (updated)




Watch “These sunglasses let you listen to music while still hearing the rest of the world” on YouTube
Free-body Diagram


Hover Camera
Why lighting circuit should be connected in parallel?
Lighting circuit, in fact all circuits at home, should be connected in parallel.
Reasons being:
When one bulb is spoilt or switched off, the rest of the bulbs can still function normally at normal brightness. This is because the potential difference across each bulb in the branches remains the same.
Refer to series and parallel circuits summary.
If the lighting circuit is connected in series, when one bulb is spoilt or switched off, it will be an open circuit and no current can flow through the circuit. Hence all the bulbs cannot function.

Factors that affect the period T of a pendulum
Period, T, is the time taken for one complete oscillation.
The period T of a pendulum is affected by the following factors.
1) the length of the pendulum:
– the longer the length, the longer the period (i.e. swing slower)
2) the gravitational field strength, g
– the greater the g, the shorter the period (i.e. swing faster)
(e.g. the g on earth is 10 N/kg while that on the moon is 1.6 N/kg, hence the period on the moon will be longer)
NOTE: (common misconceptions)
Period, T, of the pendulum is NOT affected by
1) the angle of release (as long as the angle of release is between 10 to 15 degrees)
(if the angle of release is small, the swing will not be fast and air resistance will not be significant)
2) the mass of the pendulum ball
Refer to the video below for the demonstration of the above concepts.
Pendulum: Displacement-time vs KE-time graphs
How to set up the pendulum experiment?
Click here to view the video
Gas expands and contracts the most
The 3 states of matter – solid, liquid and gas.
In general, when a body is heated, it expands and volume increases. The mass remains the same. Since density = mass/volume, its density decreases (less dense). For instance, warm air rises as it is less dense. In terms of kinetic theory, the particles will increase in kinetic energy. The average spacing between the particles increases (assuming not in a closed container).
Likewise, when a body is cooled, the opposite occurs. The body contracts and volume decreases. It becomes denser.
Due to the differences in particles arrangement of solid, liquid and gas, each expands by different amount when heated and vice versa. Which expands the most when heated and contracts the most when cooled?
The following demonstration of the ‘Pee Boy’ is a good video to show the concepts.
Explanation:
The tiny hole at the penis is too small for any water to enter on its own. So using thermal transfer in the different states, the following steps are taken:
- Put the hollow empty boy into the hot water. [air inside the boy expands more than the solid ceramic, hence bubbles are seen coming out of the hole]
- Put the hollow empty boy now into the cold water. [The air inside contracts and volume decreases. This creates a low pressure and water is then sucked into the boy through the tiny hole]
- Place the boy on a platform. [The boy is only partially filled with water. The head portion is filled air while the bottom portion is filled with water]
- Pour hot water over the head. [As the whole boy is heated by the running hot water, the air in the head portion expands much more than the water at the bottom and the solid ceramic of the boy. Hence the air pressure increases and it pushes the water out of the boy]
- And he pees!!! Quite powerful indeed!
How a fuse works?
A fuse is a safety device that is added to an electrical circuit to prevent excessive current flow. It has the same function as a circuit breaker. However , a fuse must be replaced once it melts (blows). A circuit breaker can be reset after it trips.
Electric symbol for fuse

Fuse is connected to the live wire. It consists of a short piece of thin wire. In the event of an electrical fault, when a current that exceeds its fuse rating flows through, it heats up and melts (fuse blows). When the fuse blows, the electrical appliance is disconnected from the high potential of the live wire (usually 240 V). Hence it protects the appliance and the user.
The choice of fuse is always slightly higher than the actual current flowing through the appliance, and it has to be a whole number. Typical household fuses off the shelves are rated at 1 A, 2 A, 3 A, 5 A, 10 A and 13 A. But in theory, we just state a fuse which is slightly higher and is a whole number.
Thermal Transfer Summary

Should a Person Touch 200,000 Volts? A Van de Graaff generator experiment!
Should a Person Touch 200,000 Volts? A Van de Graaff generator experiment!
Floating Bonsai Trees Are A Thing Now | CONTEMPORIST
 A perfect merger of Art and Physics!
A perfect merger of Art and Physics!
http://www.contemporist.com/2016/01/22/floating-bonsai-trees-are-a-thing-now/
Rules of Series and Parallel Circuits
Rules of Series and Parallel Circuits
 To understand direct current (DC) circuits, the best way is to think in terms of river system.
To understand direct current (DC) circuits, the best way is to think in terms of river system.
Series Circuit
Parallel Circuit
Series and Parallel Circuit
Examples:











